ABOUT OUR CLINIC
- Highly qualified professionals, including candidates of medical sciences, provide a full range of surgical and therapeutic ophthalmological services.
- Doctors of the highest category with many years of clinical experience provide diagnosis and treatment of concomitant diseases in various pathologies of the organ of vision
- The center‘s doctors are constantly improving their knowledge and introducing the latest treatment methods, regularly participate in Kazakhstani and international conferences on ophthalmology, and are members of the European Glaucoma Society (EGS)
- Услуги дневного стационара (амбулаторная хирургия)
In our clinic, experienced ophthalmologists conduct comprehensive examinations of the visual organ and specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of various eye diseases. We use the most advanced diagnostic technologies and methods to treat diseases of the visual organ, correct vision, and strive to improve people’s quality of life through improved vision. Give yourself the gift of clear vision today!
- Diagnostics:
- Visometry
- Autorefractometry
- Autokeratometry
- Tonometry
- Cycloscopy
- Ultrasound (A, B scan echography),/li>
- IOL calculation (IOLmaster 700)
- Perimetry
- Optical coherence tomography (Cirrus)
- Anterior segment analyzer (Pentacam)
The NMU Ophthalmology Center offers
Correction of ametropia (nearsightedness, farsightedness, astigmatism)
Laser:
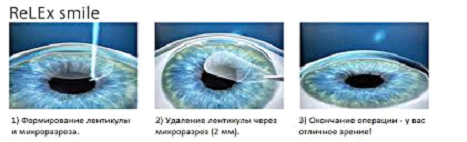
– Smile
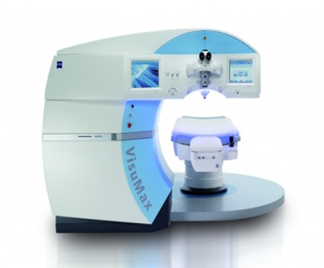
Unlike other, earlier laser procedures, no excimer laser is used here, but only a femtolaser. Without touching the surface of the cornea, the femtolaser cuts out a lenticular part in the inner layers of the cornea, which is removed through a hole a couple of millimeters in size. This method of surgery is still possible only with the Visumax femtolaser from Carl Zeiss.
– Femto-Lasik;
Visumax (Carl Zeiss)
Surgical:
– implantation of phakic IOLs;
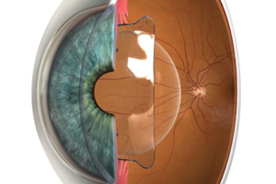
Phakic intraocular lenses:
Have a high degree of myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, thin or steep cornea become an obstacle to excellent vision?
Implantation of phakic intraocular lenses (FIOL) — the only method of surgical correction for patients with a thin cornea and myopia up to -30.0 diopters. FIOL are able to correct myopia, hypermetropia and astigmatism in cases where laser vision correction is contraindicated. It is also one of the ways to correct presbyopia. It is used only as prescribed by a doctor.
Indications:
- Myopia is about -30.0 diopters.
- Farsightedness is up to +15.0 diopters.
- Astigmatism is ±8.0 diopters.
FIOL is a flexible lens of a special shape, implanted through a micro—puncture in the cornea inside the eye in front of or behind the iris. Suturing is not required, as the puncture length is only about 2.2 mm.
When FIOL is implanted, the anatomy of the eye is not disturbed, its own lens remains intact and continues to perform its functions. The operation lasts about 10-15 minutes, and good eyesight is restored the next day.
Orthokeratological (night) lenses:
PARAGON is the first night—wear lenses that correct your vision while you sleep. Today, orthokeratology is the most modern method of contact correction of myopia and astigmatism.
The Paragon orthokeratological lens vision correction method was certified in 2002 in the USA (FDA approval) and the countries of the United Europe (CE). For three years, the specialists conducted clinical trials that proved the complete safety of using Paragon lenses. Such orthokeratological lenses can be recommended for patients from the age of six.
Paragon night–wear contact lenses provide a temporary reduction in myopia (nearsightedness) by changing the shape (alignment) of the cornea, which is elastic in nature. A slight decrease in the curvature of the cornea reduces the excessive focusing ability of the myopic eye and completely compensates for myopia.
How do night–wear lenses work?
Night–wear lenses, as well as regular contact lenses, are located directly on the mucous layer of the cornea. However, due to the special design and the shape of the reverse geometry during the time you sleep, the lenses gently affect the shape of the cornea, thereby temporarily improving vision due to a reversible change in the curvature of the cornea. Clinical trials prove that after 6-8 hours of wearing a lens, the cornea retains its altered shape for a long period of human wakefulness (up to 24 hours), so there is no need for additional correction (glasses, contact lenses) during the day. The lenses are put on 10-15 minutes before bedtime.
Cataract Surgery
Phacoemulsification of cataracts:
The most modern and least traumatic method of cataract removal today is phacoemulsification with implantation of a folding lens. This technique is performed on an outpatient basis, it is characterized by a small incision and is considered the “gold“ standard of cataract ophthalmic surgery. In addition, it does not require full maturation of the cataract and can be applied at the initial stages of its development. Phacoemulsification has no age restrictions, it can be used both in infancy and in the elderly.
Operating microscope
Cataract Removal Device
Surgical treatment of keratoconus:
Intrastromal corneal segments (IRS) are rounded implants made of medical polymer material with biocompatible properties. The diameter of the segments is about 4-6 mm, the height can vary from 150-350 microns. It is the height of the segment that determines how strong the refractive effect will be. The selection and calculation of IRS is performed by the doctor individually for the parameters of each individual patient, which allows obtaining the necessary results of visual correction.
After installing biocompatible implants in the thickness of the cornea, they begin to put pressure on the shell, giving it an anatomically correct shape, which has a positive effect on focusing and visual quality. The implants eliminate the pathological cone or other corneal shape disorders and thereby correct vision.
Intrastromal segments in keratoconus — why are they installed?
Keratoconus is a common pathology of the cornea. With this degenerative disease, dystrophy of the cornea begins. The fibers that form its structure change their characteristics, become less durable and thinner. The thinning of the cornea leads to the fact that under the influence of intraocular pressure, its tissues stretch and bulge forward. This creates an abnormal cone that prevents the image from focusing properly.
Teenagers and young people under the age of 30 are most often confronted with this problem. Factors that provoke dystrophic changes in the cornea can be heredity, disorders in the endocrine system, injuries to the visual organs and poor ecology. However, the exact cause of the disease is still unclear.
Keratoconus requires mandatory treatment, as it leads to visual impairment and a decrease in the quality of life. In addition, without timely therapy, degenerative changes progress, clouding, perforation of the corneal tissues may occur, and the disease may result in blindness.
Intravitreal administration of angiogenesis inhibitors
IVV (intravitreal injection of the drug) is a method of drug action on the deep tissues of the eye. Experience shows that instillation (instillation of drops) or the use of ointments do not have a sufficient effect on the macula (yellow spot), retina, inner membranes of the eyeball. The introduction of drugs into the blood or muscle is also often useless — the substance is likely not to pass the blood-brain barrier and will not reach the target organ. Therefore, intravitreal injection — the ability to deliver medicine directly to the site of the disease — has become one of the main ways to treat certain pathologies. Indications and contraindications for IVV An extensive category of eye diseases is treated by administering drugs intravitreally:
– Age-related macular degeneration (wet form)
– Neovascular retinal membrane on the background of high-grade myopia, damage or inflammation of the eye
– Edema of the macula (macula) and near-macular area
– Diabetic and postthrombotic retinopathy
– Blockage of the central retinal vein.
Ophthalmic laser 532 for “bottom“ pathology
Clinical application:
- Retinal photocoagulation
- Panretinal photocoagulation
- Macular photocoagulation
- Laser trabeculoplasty